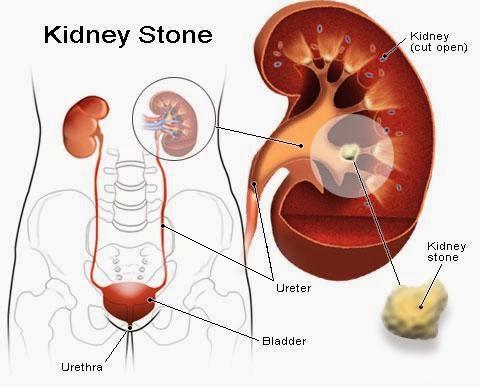
Renal Calculus – Urolithiasis – Kidney Stones
Urolithiasis denotes stones originating anywhere in the urinary
tract, including the kidneys and bladder.
The term Nephrolithiasis (or “Renal Calculus”) refers to stones that are
in the kidney, while Ureteral calculi almost always originate in the kidneys, although
they may continue to grow once they lodge in the ureter. The term
Cystolithiasis (or Vesical Calculi) refers to stones which form or have passed
into the urinary bladder.
A kidney stone, also known as a Renal Calculus is a solid
concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals
in the urine. Kidney stones typically
leave the body by passed in the urine stream and many stones are formed and
passed without causing symptoms .If stones grow to sufficient size {usually at least 3 millimeters (0.12 inch)}
they can cause obstruction of the ureter. In the pediatric population
Nephrolithiasis is an important cause of morbidity. While the exact incidence
of kidney stone disease in children is unknown, a significant increase in the
number of children diagnosed with and treated for Urolithiasis has occurred in
the last decade. In adults, kidney stones are associated with hypertension and
chronic kidney Disease. Although relatively rare in the pediatric population, recent
data regarding incidence and inpatient hospitalization rates for children with
kidney stone bring into sharp focus the need to gain a better understanding of
the metabolic underpinnings as well as environmental contributors to pediatric
Nephrolithiasis as there is high chance of recurrent stone formation.
In recent years, technological advancements have greatly
facilitated the diagnosis of stone disease. Physicians can now conclusively
identify and, perhaps more importantly, exclude stone disease within minutes of
considering the diagnosis. The management of Urolithiasis is also becoming
increasingly well defined. Clear indications for urologic referral are based on
recognition of the few urgent situations and a solid understanding of the
natural history of stone progression.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Renal colic affects approximately 1.2 million people each year
and accounts for approximately 1% of all hospital admissions.
·
The lifetime
prevalence of Nephrolithiasis estimated to be between 5% and 10%, with the
probability of having a stone varying according to age, gender, race and
geographical location.
·
Approximately
50 percent of patients with previous urinary calculi have a recurrence within
10 years.
·
About 80% of
those with kidney stones are men (male-to-female ratio of 3:1). Men most
commonly experience their first episode between 20-30years of age, while for women
the age at first presentation is somewhat later.
·
Stones due
to discrete metabolic/hormonal defect (e.g. Cystinuria, Hyperparathyroidism) and
stone disease in children are equally prevalent between the sexes.
·
Stone due to
infection (Struvite calculi) are more common in women than in men. Female
patients have a higher incidence of infected hydronephrosis.
·
Most urinary
calculi develop in persons aged 20-49 years. Peak incidence occurs in people
aged 35-45 years, but the disease can affect anyone at any age. Patients in
whom multiple recurrent stones form usually develop their first stones while in
their second or third decade of life.
·
While
Nephrolithiasis can occur in any pediatric age group, infants represent roughly
20% of pediatric stone cases and tend to have a distinct history and presentation.
·
Anatomic
abnormalities such as ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction or
ureterovesical junction (UVJ) obstruction are found on workup of Nephrolithiasis
in 11-24% of children.
·
Among
children, Nephrocalcinosis is most common in term and preterm infants who have
complicated hospital courses.
·
Children can
present with stones at any age (e.g. premature newborn to teenager).In
children, calcium stones are most common. The approximate frequence of kidney
stone types in the pediatric age group is calcium with phosphate or oxalate
(57%), struvite (24%), uric acid (8%), cystine (6%), endemic (2%), mixed (2%)
and other types (1%).
·
Approximately
40% of children with Urolithiasis have a positive family history of kidney
stones and most of the children have a metabolic background of stone disease.
·
An initial
stone attack after age 50 years is relatively uncommon.
·
Whites are
affected more often than persons of Asian ethnicity, who are affected more
often than blacks. In addition, Urolithiasis occurs more frequency in hot, arid
areas than in temperate regions.
·
In
developing countries, bladder calculi are more common than upper urinary tract
calculi; the opposite is true in developed countries. These differences are
believed to be diet-related.
RISK FACTORS
STRONG
High fat/ protein intake
·
A higher
energy diet with more fat and protein may be associated with a higher incidence
of stones. This is secondary to the increased prevalence of hyperuricouria,
hyperoxaluria and hypercalciuria associated with this diet.
High salt intake
·
Higher
sodium intake is associated with higher urinary sodium and calcium levels and
decreased citrate. This promotes calcium salt crystallization due to urinary
saturation of monosodium urate and calcium phosphate being increased. Salt also
can lead to bone loss, thereby increasing hypercalciuria.
White ancestry
·
In US men,
the highest prevalence of Nephrolithiasis is found in white men, followed by
Hispanic men, Asain men and black men. Among US women, the prevalence is
highest among white women but lowest among Asain women.
Male sex
·
Nephrolithiasis
typically affects adult men more commonly than adult women, with a male to
female ratio of 2 or 3:1.However, there is evidence that this difference in
incidence between men and women is narrowing.
Dehydration
·
Fluid intake
is very important and should be at least 2 liters per day. A low urine output
can produce higher levels of urinary solutes, leading to stone formation.
Obesity
·
Prevalence
and incident risk of Nephrolithiasis are directly correlated with weight and
BMI in both genders, although the magnitude of the association is greater in
women than in men.
·
Evidence
linking obesity with low urine pH and uric acid stones and an association with
hypercalciuria could account for an increased risk of uric acid and/ or calcium
stones in obese patients.
Crystalluria
·
Stone formers
(especially calcium oxalate stones) frequently excrete more calcium oxalate
crystals in the urine. Increased urinary excretion of crystine, struvite, and
uric acid crystals is also a risk factor for stone formation.
WEAK
Occupational exposure to dehydration
·
Dehydration
and heat exposure are risk factors for Nephrolithiasis. Those exposed to high
temperatures demonstrate lower urine volumes and pH, higher uric acid levels
and higher urine specific gravity, leading to higher urinary saturation of uric
acid, as well as calcium oxalate. As a result, people exposed to dehydration and
heated are at increased risk for forming stones.
Warm climate
·
Seasonal
variation in Nephrolithiasis is likely related to temperature because of fluid
losses through perspiration. It has been reported that the highest incidence of
Nephrolithiasis is in the summer months, July through September, with the peak
occurring within 1 to 2 months of maximal mean temperatures.
Family
history
·
A positive
family history of Nephrolithiasis is associated with an increased risk of
forming stones. A stone forming
Symptoms of kidney stones
- While some kidney stones may not
produce symptoms (known as "silent" stones), people who have
kidney stones often report the sudden onset of excruciating, cramping pain
in their low back and/or side, groin, or abdomen.
- Changes in body position do not
relieve this pain.
- The pain typically waxes and wanes
in severity, characteristic of colicky pain (the pain is sometimes
referred to as renal colic).
- It may be so severe that it is
often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Kidney stones also
characteristically cause blood in the urine.
- If infection is present in the
urinary tract along with the stones, there may be fever and chills.
Homeopathy
Medicines Treatment for Kidney Stones
Symptomatic Homeopathy works well for Kidney Stones,
It helps to prevent further recurrence also. So its good to consult a
experienced Homeopathy physician without any hesitation.
Whom to contact for Kidney Stones Treatment
Dr.Senthil
Kumar Treats many cases of Kidney Stones, In his medical professional
experience with successful results. Many patients get relief after taking
treatment from Dr.Senthil Kumar. Dr.Senthil Kumar visits Chennai at
Vivekanantha Homeopathy Clinic, Velachery, Chennai 42. To get appointment
please call 9786901830, +91 94430 54168 or mail to consult.ur.dr@gmail.com,
For
more details & Consultation Feel free to contact us.
Vivekanantha Clinic Consultation Champers
at
Chennai:- 9786901830
Panruti:- 9443054168
Pondicherry:- 9865212055 (Camp)
For appointment please Call us or Mail Us
For appointment: SMS your Name -Age – Mobile Number - Problem in Single word -
date and day - Place of appointment (Eg: Rajini – 30 - 99xxxxxxx0 – Kidney
Stones – 21st Oct, Sunday - Chennai ), You will receive Appointment details
through SMS
==--==